From our sister journals – July 2016
Posted by the Node, on 25 July 2016
Here we highlight some developmental biology related content from other journals published by The Company of Biologists.

Aging zebrafish an ideal model
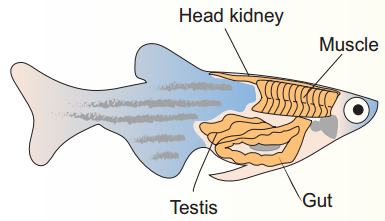 Mice have been the traditional model of choice
Mice have been the traditional model of choice
for investigating telomere shortening in aging, but zebrafish provide an upcoming complementary system with well-conserved physiology. Ferreira and colleagues discuss how fishes have helped our understanding of how telomere attrition contributes to cellular senescence, organ dysfunction and disease. [OA]
Diverse phenotypes in neurofibromatosis models
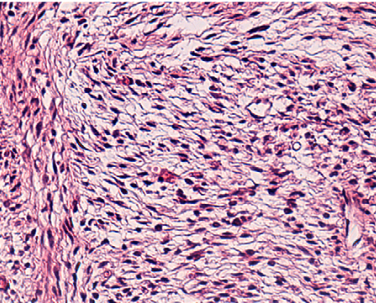 Neurofibromatosis type 1 is characterised by nerve sheath tumours but also has significant clinical heterogeneity. Robert Kesterson and colleagues show that two mouse models carrying NF1 patient-specific mutations have distinct effects on embryonic development, neurofibromin function and plexiform neurofibroma formation, with implications for therapeutic studies. [OA]
Neurofibromatosis type 1 is characterised by nerve sheath tumours but also has significant clinical heterogeneity. Robert Kesterson and colleagues show that two mouse models carrying NF1 patient-specific mutations have distinct effects on embryonic development, neurofibromin function and plexiform neurofibroma formation, with implications for therapeutic studies. [OA]

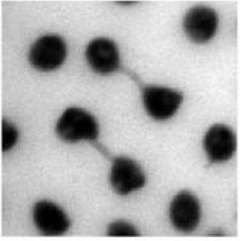 Maternal effects of chromosomal abnormalities
Maternal effects of chromosomal abnormalities
Early emerging problems during oogenesis, such as DNA double-strand breaks, can affect chromosome duplication and segregation in embryogenesis in Drosophila, Andreas Kegel and
colleagues report. Moreover, environmental cues including temperature are important for proper oogenesis. [OA]
Antibodies light up membrane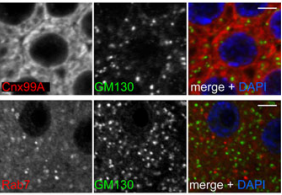 traffic
traffic
Sean Munro and
colleagues report the generation and
characterisation of a toolkit of
monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies for labelling the major compartments of the secretory and endocytic pathways in flies, and demonstrate their applicability in multiple cell types. [OA]

S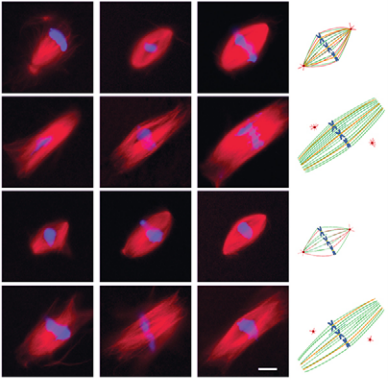 perm centrosomes defines spindle assembly
perm centrosomes defines spindle assembly
Isabelle Vernos and colleagues use a Xenopus egg extract system to analyse how the first embryonic spindle is formed, and find that the duplicated sperm centrosomes define the kinetics of spindle bipolarization, ensuring their own inheritance to the daughter cells.
Probing chromatin in living cells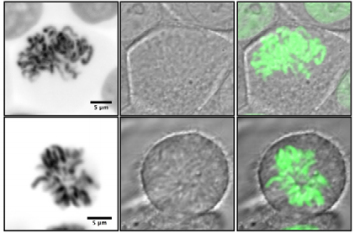
Gladys Mirey and colleagues present Chromatibody, a
genetically encoded single-domain antibody that binds in a non-invasive manner to the heterodimer of H2A-H2B histones across eukaryotes. This tool allows real time chromatin imaging across eukaryotes, as well as a means to target proteins to chromatin. [OA]
An overview of Myosin-I motors
In their Cell Science at a Glance poster and article, Betsy McIntosh and Michael Ostap illustrate the proposed functions of metazoan myosin-I molecular motors, examining structural, biochemical, mechanical and cell biological evidence.
Smaller broods promote quicker endothermy
Jan-Åke Nilsson and colleagues show that the ability of blue tit chicks to generate their own body heat is influenced by the size of the brood they grow up in, with chicks from smaller broods becoming endothermic earlier than those from larger broods.



 (No Ratings Yet)
(No Ratings Yet)