From our sister journals – May 2016
Posted by the Node, on 26 May 2016
Here is some developmental biology related content from other journals published by The Company of Biologists.
Gastrointestinal stem cells in health and disease
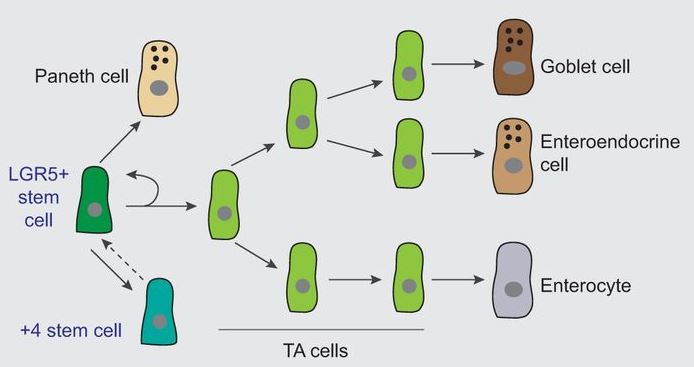 This Review from Li and Jasper highlights recent findings on intestinal stem cell (ISC) diversity in the GI tract of Drosophila, focusing on the role of ISCs in healthy and diseased conditions, and drawing parallels with vertebrate GI stem cells. Read the paper here [OPEN ACCESS].
This Review from Li and Jasper highlights recent findings on intestinal stem cell (ISC) diversity in the GI tract of Drosophila, focusing on the role of ISCs in healthy and diseased conditions, and drawing parallels with vertebrate GI stem cells. Read the paper here [OPEN ACCESS].
TET-1 in neural tube closure
Lozanoff and colleagues propose an epigenetic mechanism establishing the regulation of genes that are crucial for neural tube closure. This mechanism could be a novel target for resolving such birth defects and associated disorders. Read the paper here [OPEN ACCESS].
 Genetic variants of zebrafish muscle myosin
Genetic variants of zebrafish muscle myosin
Pack and co-workers report two newly identified Myh11 gene missense mutations discovered in a zebrafish enhancer-suppressor mutagenesis screen. The mutations disrupt myosin regulation and ATPase activity in a graded fashion, and this correlated with their effects on intestinal and vascular physiology. Read the paper here [OPEN ACCESS].
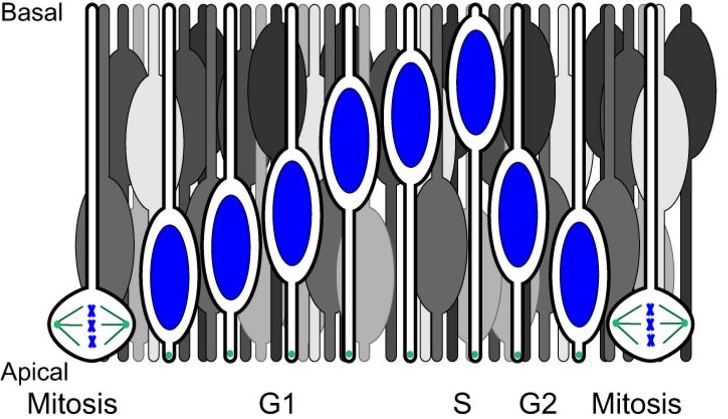 Nuclear migration events in development
Nuclear migration events in development
Nuclear migration is a central part of many cell and developmental processes. Bone and Starr review the large number of different molecular mechanisms that exist to move nuclei to specific, intracellular locations. Read the paper here.
TrkA mediates Sema3A signalling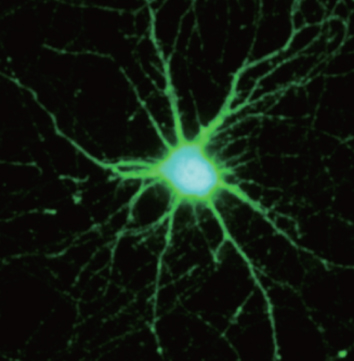
Goshima and colleagues show that, by interacting with PlexA4, TrkA plays a crucial role in redirecting local Sema3A signaling to retrograde axonal transport, thereby regulating dendritic GluA2 localization and patterning. Read the paper here.
Epiboly expands the mammalian epidermis
Formstone and co-workers find that the nascent mammalian epidermis spreads to enclose the embryo trunk through a process akin to epiboly, which has important implications for human birth defects of the abdominal wall. Read the paper here [OPEN ACCESS].
Tadpole eyes swivel and cross during metamorphosis
Combes and colleagues analyse adaptive neural plasticity of spinal locomotor-extraocular motor circuit coupling that enables Xenopus frogs to continuously generate effective retinal image-stabilizing eye movements throughout the metamorphic transition from fish-like tadpole to quadrupedal adult. Read the paper here.
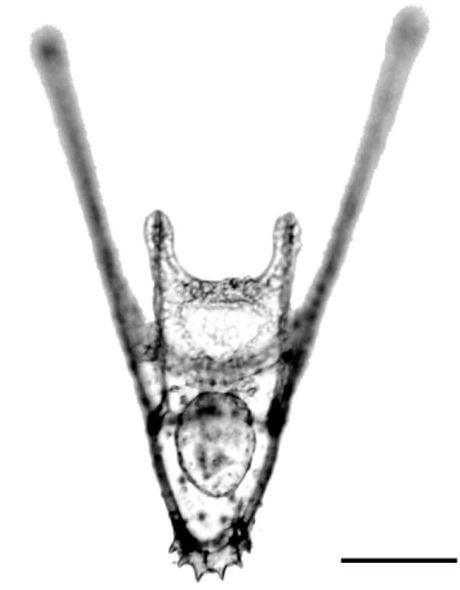 Extra arms destabilise sea urchin larvae
Extra arms destabilise sea urchin larvae
Chan and co-workers show that pre-competent, 6-armed larval urchins swim faster and are less stable in experimental turbulent flow than younger 4-armed larvae, suggesting a potential age/morphology-driven differential transport mechanism in ambient flow conditions. Read the paper here [OPEN ACCESS].

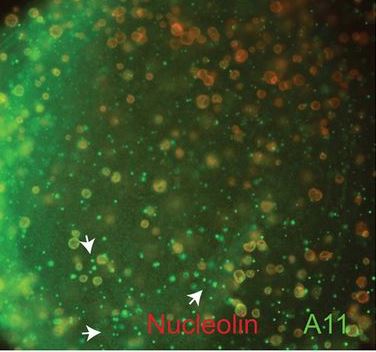 Amyloid assembley in Xenopus oogenesis
Amyloid assembley in Xenopus oogenesis
Hayes and Weeks find that non-membrane-bound nuclear particles in Xenopus oocytes responsible for RNA transcription, modification and processing contain proteins assembled into amyloids as part of normal development. Read the paper here [OPEN ACCESS].





 (1 votes)
(1 votes)