Building blocks
Posted by Erin M Campbell, on 19 October 2010
Somites are the building blocks of the vertebrae, skeletal muscle and dermis…literally and figuratively. Somites define the segmented features of vertebrate embryos, and are repeated blocks of epithelial cells formed sequentially, from anterior to posterior, and at regular intervals on either side of the neural tube. A paper in the November 1 issue of Development helps our understanding of the signaling cascade that acts during somitogenesis.
Integrins are transmembrane proteins that function in cell adhesion, migration, signaling and proliferation, which are all important processes during development. Previous research had demonstrated a role for integrins in the formation of somites in certain organisms, but the exact requirement or mechanism was not clear. This month in Development, Rallis and colleagues show that β1-integrin is important for formation of all somites in chick embryos. They also found that β1-integrin functions in “outside-inside” signaling, meaning that signals from the extracellular matrix bind to integrins and result in the activation of signaling within the cell. Specifically, β1-integrin functions cell-autonomously to activate Wnt and Notch signaling, via ILK, which leads to compartmentalization and boundary formation of somites.
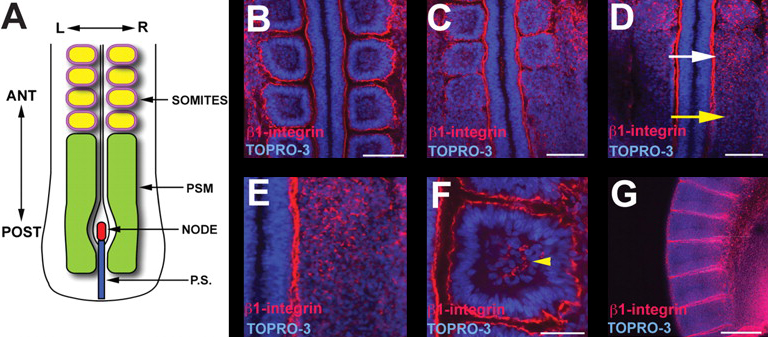
Images above show a schematic of a chick embryo (A) and β1-integrin (red) localization during somite formation (TOPRO3, in blue, stains nuclei and shows somite organization). β1-integrin was found at the borders of both older, anterior somites (B) and newly formed somites (C). There was also an anterior-posterior gradient of β1-integrin in the presomitic mesoderm prior to somite formation (white versus yellow arrow in D, and zoomed image in E). Interestingly, β1-integrin was found in the core of somites (F, arrowhead), and showed a continued segmented pattern in much later embryos (G).
Reference: Charalampos Rallis, Sheena M. Pinchin and David Ish-Horowicz (2010). Cell-autonomous integrin control of Wnt and Notch signalling during somitogenesis. Development 137, 3591-3601. Paper can be found here.


 (9 votes)
(9 votes)