Worms teach about germline stem cells
Posted by Erin M Campbell, on 10 October 2012
 To me, the stem cells within a germline are a perfect storm of fascination. Stem cells are, of course, intriguing in their ability to self-renew and differentiate, and a germline is intriguing in its ability to generate gametes. Add stem cells and germlines together, and you have amazing biology in front of you…and more biology to discover and understand. Today’s images are from a paper describing mRNA regulation in germline stem cells in C. elegans.
To me, the stem cells within a germline are a perfect storm of fascination. Stem cells are, of course, intriguing in their ability to self-renew and differentiate, and a germline is intriguing in its ability to generate gametes. Add stem cells and germlines together, and you have amazing biology in front of you…and more biology to discover and understand. Today’s images are from a paper describing mRNA regulation in germline stem cells in C. elegans.
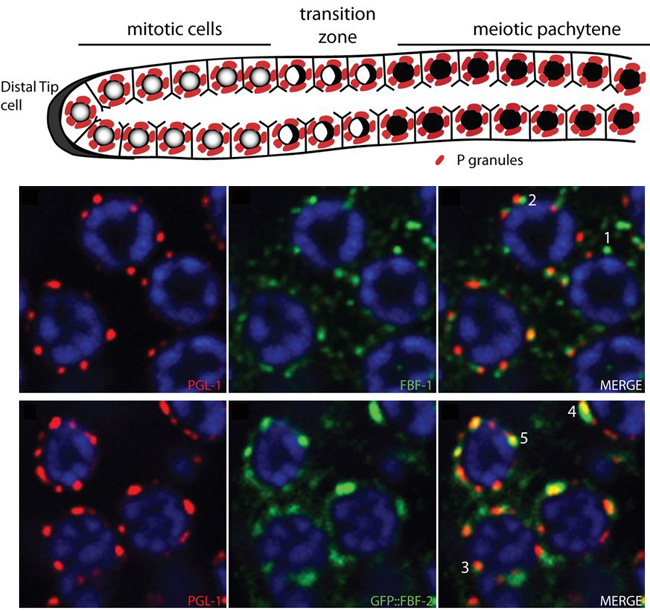
The C. elegans germline is set up as a U-shaped tube of differentiation and gamete production. At the distal end of the germline, a niche of stem cells constantly divides throughout the life of the worm. These mitotically dividing cells get pushed along the germline as more cells are produced, and accumulate low levels of meiotic proteins until entering the transition zone in preparation for meiosis. P-granules are RNA granules, or nuage, found within the C. elegans germline. P-granules localize to the nuclear envelope and have been suggested to directly regulate mRNAs exported from the nucleus, as a form of post-transcriptional control over gene expression. A recent paper describes results showing the importance of P-granules in mRNA regulation within germline stem cells. Voronina and colleagues show that two 89% identical PUF family RNA-binding proteins, FBF-1 and FBF-2, have important and distinct functions in regulating meiotic mRNAs. FBF-1 regulates the degradation or transport of meiotic mRNAs out of the stem cell region, while FBF-2 prevents translation of meiotic mRNAs. In addition, Voronina and colleagues found that FBF-2 is dependent on PGL-1, a P-granule component, for proper nuclear localization and binding to target mRNAs. The use of different mechanisms to prevent meiotic protein expression within the stem cell region ensures that the germline can function properly.
The cartoon above shows the different zones of the germline, with germline stem cells dividing in a niche at the distal end (left side). The images show the nuclei (blue) of cells in the mitotic zone in the germline. FBF-1 (green, top) and FBF-2 (green, bottom) are found at distinct foci around the nuclei. FBF-2 is found primarily on P-granules (PGL-1, red, bottom row).
For a more general description of this image, see my imaging blog within EuroStemCell, the European stem cell portal.
![]() Ekaterina Voronina, Alexandre Paix, & Geraldine Seydoux (2012). The P granule component PGL-1 promotes the localization and silencing activity of the PUF protein FBF-2 in germline stem cells. Development, 139 (20), 3732-3740 DOI: 10.1242/dev.083980
Ekaterina Voronina, Alexandre Paix, & Geraldine Seydoux (2012). The P granule component PGL-1 promotes the localization and silencing activity of the PUF protein FBF-2 in germline stem cells. Development, 139 (20), 3732-3740 DOI: 10.1242/dev.083980


 (1 votes)
(1 votes)