From our sister journals- February 2016
Posted by the Node, on 22 February 2016
Here is some developmental biology related content from other journals published by The Company of Biologists.
Using the developmental biology toolkit to study cancer
 review the similarities between embryogenesis and cancer progression and discuss how the concepts and techniques of developmental biology are being applied to provide insight into all aspects of tumorigenesis. Read the review here [OPEN ACCESS].
review the similarities between embryogenesis and cancer progression and discuss how the concepts and techniques of developmental biology are being applied to provide insight into all aspects of tumorigenesis. Read the review here [OPEN ACCESS].
A new gestational diabetes mellitus model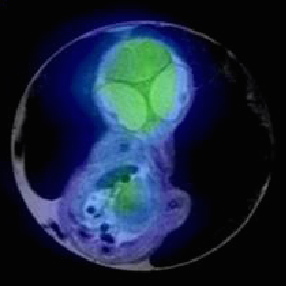
He and colleagues successfully establish a new chick embryo model to study the molecular mechanism of hyperglycemia-induced eye malformation. Read the paper here [OPEN ACCESS].
Cathepsin D sorting in neurons
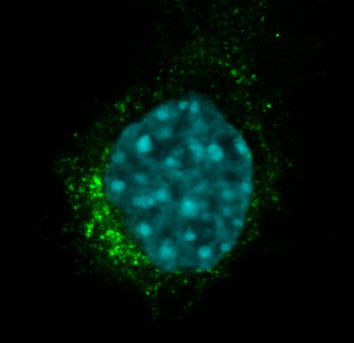
Jadot and colleagues show that SEZ6L2 can serve as a receptor to mediate the sorting of cathepsin D to endosomes, and that this sorting process might contribute to neuronal development. Read the paper here.
Demethylase activity in ESC differentiation
Becker and colleagues show that KDM6-specific H3K27me3 demethylase activity is crucially involved in the DNA damage response and survival of differentiating murine ESCs. Read the paper here.
Hic-5 in angiogenesis and myofibroblast differentiation
Two studies investigate the role of focal adhesion protein Hic-5. Bayless and colleagues examine whether Hic-5 regulates endothelial sprouting in three dimensions (here), while Van De Water and co-workers report a crucial role for this protein in myofibroblast differentiation in response to TGF-β (here).
A role for miR-20a in endothelial-mesenchymal transition
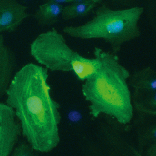 Krenning and colleagues show that FGF2 induces the expression of miR-20a, a non-coding microRNA identified in a previous screen, which targets the TGFβ receptor complex and abolishes endothelial–mesenchymal transition. Read the paper here.
Krenning and colleagues show that FGF2 induces the expression of miR-20a, a non-coding microRNA identified in a previous screen, which targets the TGFβ receptor complex and abolishes endothelial–mesenchymal transition. Read the paper here.
Characterising the fourth WASP
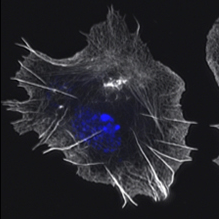 Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome proteins (WASPs) are nucleation-promoting factors that differentially control the Arp2/3 complex. Here, Bogdan and colleagues characterized WHAMY, the fourth Drosophila WASP family member, and show that it plays a role in myoblast fusion, macrophage cell motility and sensory organ development in Drosophila. Read the paper here.
Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome proteins (WASPs) are nucleation-promoting factors that differentially control the Arp2/3 complex. Here, Bogdan and colleagues characterized WHAMY, the fourth Drosophila WASP family member, and show that it plays a role in myoblast fusion, macrophage cell motility and sensory organ development in Drosophila. Read the paper here.
Loss of PPARγ leads to impaired angiogenesis
Loss of PPARγ in mice leads to osteopetrosis and pulmonary arterial hypertension in mice, and is associated with vascular disease. Alastalo and colleagues now report a novel mechanism by which PPARγ can regulate endothelial cell homeostasis and angiogenesis. Read the paper here.
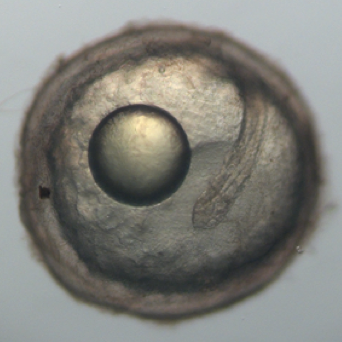 The embryos of Austrofundulus limnaeus, a killifish that resides in ephemeral ponds, routinely enter diapause II, a reversible developmental arrest promoted by endogenous cues rather than environmental stress. Toni and Padilla use A. limnaeus to examine epigenetic features associated with embryonic arrest. Read the paper here.
The embryos of Austrofundulus limnaeus, a killifish that resides in ephemeral ponds, routinely enter diapause II, a reversible developmental arrest promoted by endogenous cues rather than environmental stress. Toni and Padilla use A. limnaeus to examine epigenetic features associated with embryonic arrest. Read the paper here.





 (No Ratings Yet)
(No Ratings Yet)