From our sister journals- March 2016
Posted by the Node, on 18 March 2016
Here is some developmental biology related content from other journals published by The Company of Biologists.
Drosophila as a model to study human disease
 The latest issue of Disease Models & Mechanisms highlights the translational impact of Drosophila research. In this issue, Moulton and Letsou review several Drosophila models of human inborn errors of development (read here), while the poster and review by Bellen and colleagues examine some of the tools and assays available in Drosophila to study human disease (read here).
The latest issue of Disease Models & Mechanisms highlights the translational impact of Drosophila research. In this issue, Moulton and Letsou review several Drosophila models of human inborn errors of development (read here), while the poster and review by Bellen and colleagues examine some of the tools and assays available in Drosophila to study human disease (read here).
Nanog suppresses senescence
 Thummer, Edenhofer and colleagues analysed the outcomes of Nanog gain-of-function in various cell models employing a recently developed cell-permeant version of this protein. They show that Nanog blocks cellular senescence of fibroblasts through transcriptional regulation of cell cycle inhibitor p27KIP1. Read the paper here [OPEN ACCESS].
Thummer, Edenhofer and colleagues analysed the outcomes of Nanog gain-of-function in various cell models employing a recently developed cell-permeant version of this protein. They show that Nanog blocks cellular senescence of fibroblasts through transcriptional regulation of cell cycle inhibitor p27KIP1. Read the paper here [OPEN ACCESS].
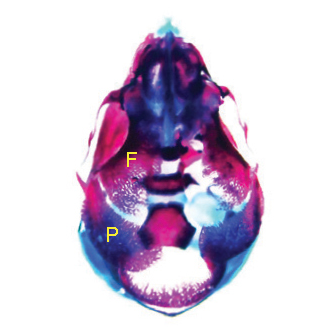 Skeletal development
Skeletal development
Panx3 and Cx43 are two important gap junction proteins expressed in osteoblasts. Yamada and colleagues show that Panx3 and Cx43 regulate skeletal formation through their distinct expression patterns and functions. Read the paper here.
Asymmetric cell division in the worm
Phillips and colleagues show that two Dishevelled paralogs have both redundant and non-redundant roles in β-catenin regulation during asymmetric cell division in C. elegans. Read the paper here.
 MOBP in oligodendrocyte differentiation
MOBP in oligodendrocyte differentiation
Myelin-associated oligodendrocytic basic protein (MOBP) resembles myelin basic protein (MBP), but the signals initiating its synthesis and function remain elusive. In this paper, White and colleagues show, by several approaches in cultured primary oligodendrocytes, that MOBP synthesis is stimulated by Fyn activity, and reveal a new function for MOBP in oligodendroglial morphological differentiation. Read the paper here.
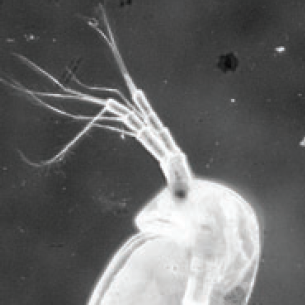 How bacteria can affect development
How bacteria can affect development
Mushegian and colleagues examined the effect of temperature and presence of bacteria in diapausing eggs of the water flea Daphnia magna. They show that the presence of bacteria increases successful development of resting eggs at an elevated temperature. Read the paper here.
Water deprivation affects snake development
Dupoué and colleagues examined the effects of water availability on corticosterone secretion in breeding snakes. They show that water deprivation induces an increase in baseline corticosterone level in pregnant aspic vipers, which may subsequently influence offspring growth. Read the paper here.

Controlling tissue polarity
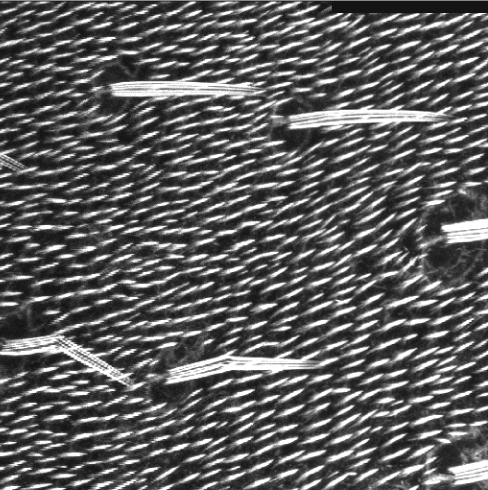 Planar cell polarity sigalling directs the polarization of cells within the plane of many epithelia. examine the signals that Prickle and Spiny-legs respond to and the mechanisms they use to control the direction of tissue polarity in the distal wing and the posterior abdomen of Drosophila. Read the paper here [OPEN ACCESS].
Planar cell polarity sigalling directs the polarization of cells within the plane of many epithelia. examine the signals that Prickle and Spiny-legs respond to and the mechanisms they use to control the direction of tissue polarity in the distal wing and the posterior abdomen of Drosophila. Read the paper here [OPEN ACCESS].
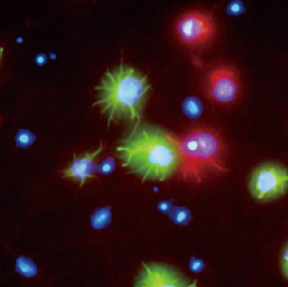 From fibroblasts to neural crest
From fibroblasts to neural crest
Motohashi and colleagues identified the transcription factors specifically expressed in developing mouse neural crest cells, and showed that SOX10 and SOX9 directly converted fibroblasts into neural crest cells. Read the paper here [OPEN ACCESS].





 (No Ratings Yet)
(No Ratings Yet)