2010 was declared the International Year of Biodiversity by the UN. At the Science & Culture Department of Montpellier University, which has designed science outreach and public engagement projects since 2000, we wanted to mark the occasion with an original project. We wanted a project that would:
– talk about the methods rather than the results of the scientific process
– explain the techniques used by naturalists to study biodiversity (past-present-future)
– develop a do it at home project (with no need for an expedition to a remote deserted island)
– have fun with disciplines often perceived as “dry”, such as taxonomy, phylogeny, classification…
– work with kids and families (adults included)
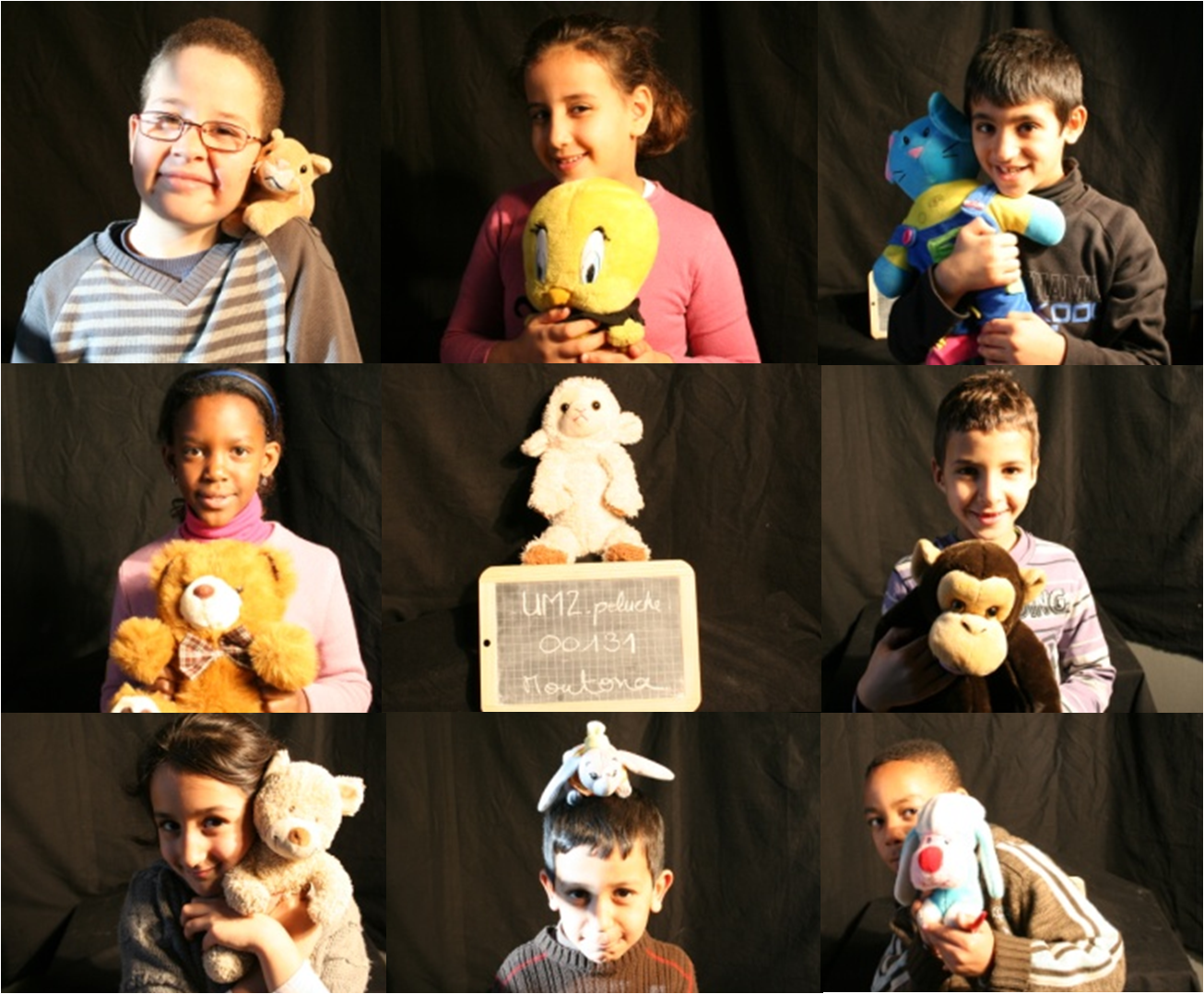
As the result of a previous exhibition on evolution where we could evaluate the pedagogic potential of soft toys, we decided to create a fake (but highly serious) Société Française de Peluchologie-French Plushology Society, supposedly created in 1903, year of the creation of the first teddy bear. The idea being to study soft toys using the methods of a naturalist. Following this mysterious scientific discipline, kids (and adults) were encouraged to bring in and study specimens carefully. In the process they transformed a random collection of soft toys into scientific collections! Participants named specimens using Linnean binomial nomenclature (leading to very funny proposals), measured their specimens, compared them, and attempted to set up a real scientific collection and classification.

French Plushology Society, est 1903
The idea behind the project is that soft toys are part of every one of us (our first “transitional friend” was probably a soft toy [1]). Moreover, during childhood (and later for many of us…), stuffed animals are part of our “imaginary ecosystem”;
We created a 200m2 exhibition with display cabinets, interactive multimedia, and posters created in collaboration with master students in environmental sciences. We worked with a DNA phylogeny research group of researchers at our University on the classification process. We also convinced scientists to describe on a video their favourite soft toy, and use it to explain a specific aspect of evolution (bacteria soft toys and co-evolution, armadillo and genetic phylogeny, worms and parasitology…).
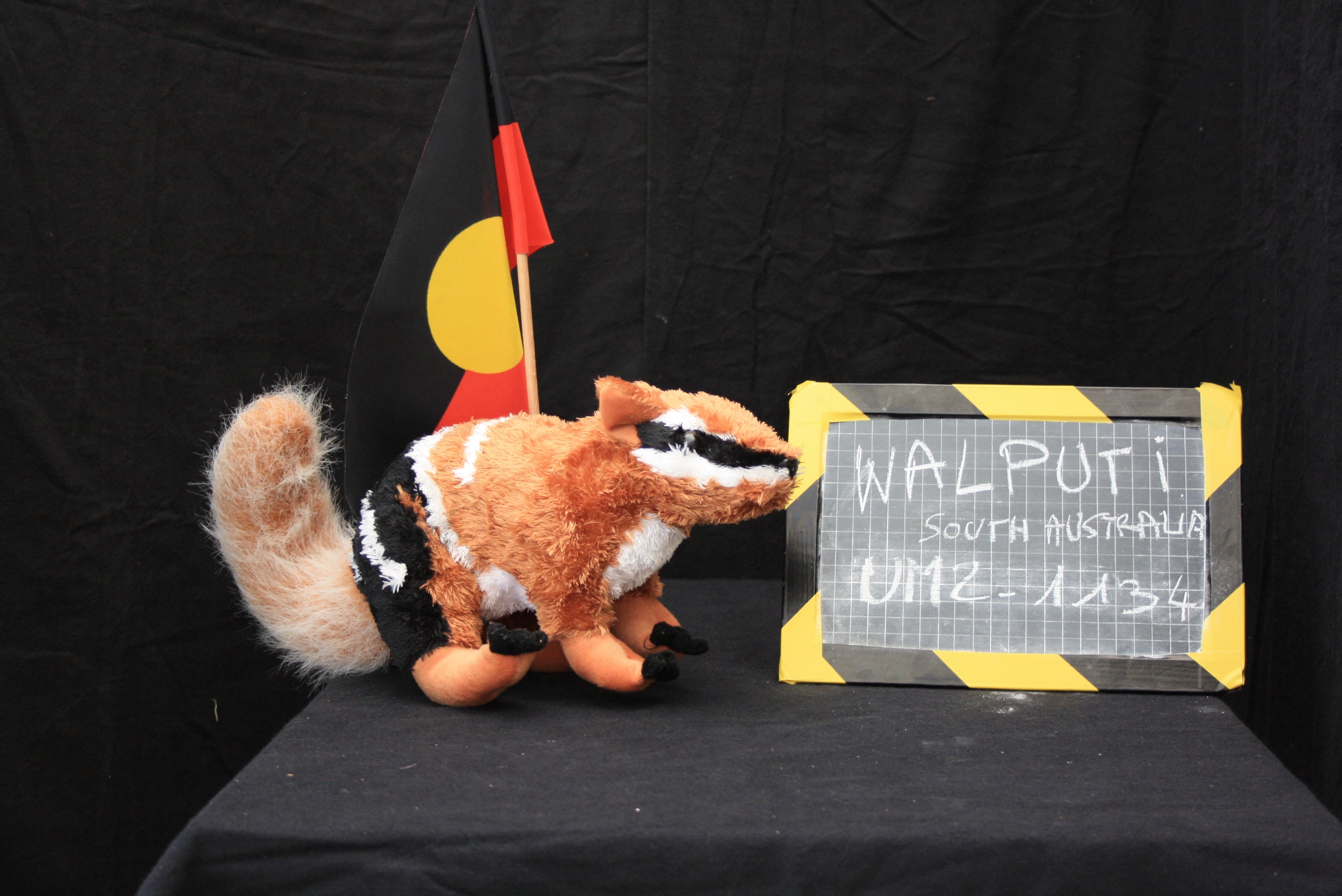

Our own collection has grown over time, by regular trips to second-hand shops and many spontaneous donations during activities. Some nice soft toys were also sent by collaborators all around the globe to illustrate local specimens. We have also collaborated with the 13th congress of the International Society of Ethnobiology (held in Montpellier in 2012), with conference attendees sharing with us their original toys…
Soft toys are really nice educational tools to explain a variety of biodiversity concepts. We start with specimen description: size, colour, material, label… Then, for the classification process, we list the characteristics without ordering them (colour, 4 legs, 2 legs, round ears, tail,…) coded by a O (absence)/1(presence) scale on a table. We then group the most similar specimens. I can tell you that agreements and deliberations within groups are not so far from discussions held in the genetic phylogeny labs! A plushology workshop on classification usually leads to many heated discussions: “let’s first classify by number of legs rather than colour”. This ability to re-invent a system collaboratively is a very interesting process..

Almost any aspect of evolution can be easily explored with the right soft toy specimens: adaptation can be explained by soft toys with magnets, that are able to invade the fridge ecosystem; convergence can be explained using different striped soft toys; antique and recent teddy bears can introduce concepts of evolution; a souvenir moose soft toy can be an endemic species of Canada; extinction can be explained using a dodo soft toy from the island of Mauritius; classification challenges can be illustrated using a platypus soft toy; examples of invasive species are the Olympic games or world cup mascots (and of course Hello Kitty); and so on…
We take great care to preserve the poetry and emotions of soft toys, especially with the youngest public. However, it is REALLY important not to mix real and imaginary animals : the soft toys have to be studied as “soft objects” and not as dolphins or tigers…

Looking at soft toys can give an unrealistic vision of “real“ biodiversity. For example, the soft toy ecosystem has a considerable mammal content (especially bears!) but almost no insects. In the wild, biodiversity is mostly composed of insects (600,000 species) and the mammal proportion (6,000 species) is very small… So, soft toys diversity can deliver an incorrect idea of the variety of living species surrounding us.
However, the differences between the world of soft toys and real biodiversity can be the starting point to introduce concepts in an original way. One of the things that you may have spotted is that soft toys do not reproduce sexually. However, it is quite easy to explain that the vast majority of them are industrially cloned in China, and artists still create some of them manually (often made from natural material such as mohair and alpaca). In fact, the supply and demand laws of economics, designer inspiration and buyers’ tastes are perfectly Darwinian in our opinion. As an example: teddy bears’ forearms shortened during World War I due to the scarcity of raw materials.
This project is highly flexible and can be adapted to many different kinds of events. We have presented our project in a street theatre festival that focused on the theme of “Monsters” (setting up a monster soft toy collection), as well as in a municipal biodiversity fiesta (installing soft toys in a tree and organizing a binocular-assisted study of the zone, as well as tree climbing). We have even organized the first “plushology masters exam”. One of the question asked to draw the hotspots and deserts of soft toys on a blank worldmap. A diploma ceremony (in collaboration with the head of studies) even took place at the University.
The success and experience acquired in these activities gave us the idea to invade the web with our project. We decided to launch a collaborative platform where anyone can geo-localize their preferred toy and share their discoveries with the plushologist community. To date (November 2014), 1618 specimens have been described. The number is of course less important than the process…

A masters student at Montpellier University has also decided to work out the “king of soft toys” teddy bear classification. One can discover online which family his/hers favourite teddy belongs to, progressing step by step through a friendly cladistic tree.
Plushology is a wonderful and open-ended collaborative experiment. An original way to explore (bio)diversity through the scientific study of an imaginary ecosystem. The Plushologist community is growing worldwide, and the national Portuguese Science Explainers Association is currently launching a local project. Plushology is a great way to involve kids in science activities, and a really fun way to approach not so funny disciplines such as taxonomy, phylogeny, cladistics and classification.
And remember: “everyone has a soft toy story to tell”…
Videos (in french):
And also this video.
Links:
Mission Peluche website: http://www.peluche.um2.fr
Article: Plushology, a soft science (in French) : http://ocim.revues.org/1015
A collaboration with “Improbable Research”: http://www.improbable.com/2013/07/05/towards-a-taxonomy-of-teddy-bears/
Reference:
1- Transitional object explanation, on wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Comfort_object
 This post is part of a series on science outreach. You can read the introduction to the series here and read other posts in this series here.
This post is part of a series on science outreach. You can read the introduction to the series here and read other posts in this series here.
 (8 votes)
(8 votes)
 Loading...
Loading...


 (5 votes)
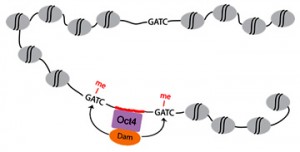
(5 votes) The nervous system of bilaterians arises from a small pool of neural progenitor cells (NPCs) that expressesSoxB genes, a family of transcription factors crucial for neurogenesis. The existence of NPCs has thus far been described in diverse species of Bilateria but not in its sister group, the Cnidaria. Hence, the evolutionary origin of NPCs remains obscure. Gemma Richards and Fabian Rentzsch (p.
The nervous system of bilaterians arises from a small pool of neural progenitor cells (NPCs) that expressesSoxB genes, a family of transcription factors crucial for neurogenesis. The existence of NPCs has thus far been described in diverse species of Bilateria but not in its sister group, the Cnidaria. Hence, the evolutionary origin of NPCs remains obscure. Gemma Richards and Fabian Rentzsch (p.  Continuous neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus is achieved by a tightly regulated balance between adult neural stem cell (aNSCs) self-renewal and differentiation. aNSC self-renewal is maintained by the action of ‘stemness’ genes, including Notch. Conversely, aNSC differentiation involves both the inactivation of the ‘stemness’ genes and activation of pro-neural genes. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis is regulated by intrinsic stimuli such as epigenetic modifications, as well as extrinsic inputs such as exercise, diet or hypoxia, which ultimately cause metabolic stress. However, the molecular mechanisms linking metabolic changes to the epigenetic control of aNSCs remain unclear. Using genetic ablation and pharmacological manipulation in mouse (p.
Continuous neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus is achieved by a tightly regulated balance between adult neural stem cell (aNSCs) self-renewal and differentiation. aNSC self-renewal is maintained by the action of ‘stemness’ genes, including Notch. Conversely, aNSC differentiation involves both the inactivation of the ‘stemness’ genes and activation of pro-neural genes. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis is regulated by intrinsic stimuli such as epigenetic modifications, as well as extrinsic inputs such as exercise, diet or hypoxia, which ultimately cause metabolic stress. However, the molecular mechanisms linking metabolic changes to the epigenetic control of aNSCs remain unclear. Using genetic ablation and pharmacological manipulation in mouse (p.  In both plants and animals, cellular senescence is not only an age-related process, but can also contribute to developmental programs. In plants, senescence can occur with age and in response to suboptimal growing conditions to reallocate nutrients from the leaves to the developing parts of the plant, particularly to maturing seeds. However, the interplay between age- or environmentally induced senescence and developmental programs is still unclear. Using a ChIP-Seq approach in Arabidopsis (p.
In both plants and animals, cellular senescence is not only an age-related process, but can also contribute to developmental programs. In plants, senescence can occur with age and in response to suboptimal growing conditions to reallocate nutrients from the leaves to the developing parts of the plant, particularly to maturing seeds. However, the interplay between age- or environmentally induced senescence and developmental programs is still unclear. Using a ChIP-Seq approach in Arabidopsis (p.  During development, somites form by periodic budding from the pre-somitic mesoderm (PSM), and give rise to the vertebral column and most of the muscles and skin. This process is driven by the pulsatile expression of ‘clock genes’, the expression of which is synchronized across the PSM. This synchronicity is regulated by the Notch pathway. Notch1 and its ligand Delta1 (Dll1) are reported to be expressed in a continuous gradient in the PSM and it is unclear how these static receptor and ligand profiles can drive and synchronise pulsatile gene expression. Through experiments in mouse and chick (p.
During development, somites form by periodic budding from the pre-somitic mesoderm (PSM), and give rise to the vertebral column and most of the muscles and skin. This process is driven by the pulsatile expression of ‘clock genes’, the expression of which is synchronized across the PSM. This synchronicity is regulated by the Notch pathway. Notch1 and its ligand Delta1 (Dll1) are reported to be expressed in a continuous gradient in the PSM and it is unclear how these static receptor and ligand profiles can drive and synchronise pulsatile gene expression. Through experiments in mouse and chick (p.  Building the elaborate neural networks required for brain function involves profound cytoskeleton remodelling during axonal growth and pathfinding. In particular, axonal growth is supported by the growth cone, a dynamic F-actin based structure, and regulated by ADF/Cofilin, an F-actin destabilising protein. Cofilin is activated by dephosphorylation by Slingshot (Ssh), and inhibited by LIMK-mediated phosphorylation. Activity of these regulators is in turn influenced by the small GTPase Rac, which acts via Pak to promote LIMK activity and inhibit Cofilin, but also via a Pak-independent, non-canonical pathway to promote Cofilin activity. However, the molecular mediators of the non-canonical pathway are currently unknown. Here (p.
Building the elaborate neural networks required for brain function involves profound cytoskeleton remodelling during axonal growth and pathfinding. In particular, axonal growth is supported by the growth cone, a dynamic F-actin based structure, and regulated by ADF/Cofilin, an F-actin destabilising protein. Cofilin is activated by dephosphorylation by Slingshot (Ssh), and inhibited by LIMK-mediated phosphorylation. Activity of these regulators is in turn influenced by the small GTPase Rac, which acts via Pak to promote LIMK activity and inhibit Cofilin, but also via a Pak-independent, non-canonical pathway to promote Cofilin activity. However, the molecular mediators of the non-canonical pathway are currently unknown. Here (p.  Quiescence has been proposed as a fundamental property of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), acting to protect them from functional exhaustion and cellular insults to enable lifelong hematopoietic cell production. Toshio Suda and colleagues review the current methods available to measure quiescence in HSCs and discuss the roles and regulation of HSC quiescence. See the Review on p.
Quiescence has been proposed as a fundamental property of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), acting to protect them from functional exhaustion and cellular insults to enable lifelong hematopoietic cell production. Toshio Suda and colleagues review the current methods available to measure quiescence in HSCs and discuss the roles and regulation of HSC quiescence. See the Review on p.  Transcription factors establish the tremendous diversity of cell types in the nervous system by regulating the expression of genes that give a cell its morphological and functional properties. Celine Santiago and Greg Bashaw highlight recent work that has elucidated the functional relationships between transcription factors and the downstream effectors through which they regulate neural connectivity in multiple model systems. See the Review on p.
Transcription factors establish the tremendous diversity of cell types in the nervous system by regulating the expression of genes that give a cell its morphological and functional properties. Celine Santiago and Greg Bashaw highlight recent work that has elucidated the functional relationships between transcription factors and the downstream effectors through which they regulate neural connectivity in multiple model systems. See the Review on p.  (No Ratings Yet)
(No Ratings Yet)







 (7 votes)
(7 votes)